Ground-Mounted vs. Roof-Mounted Solar: Which Is Better?
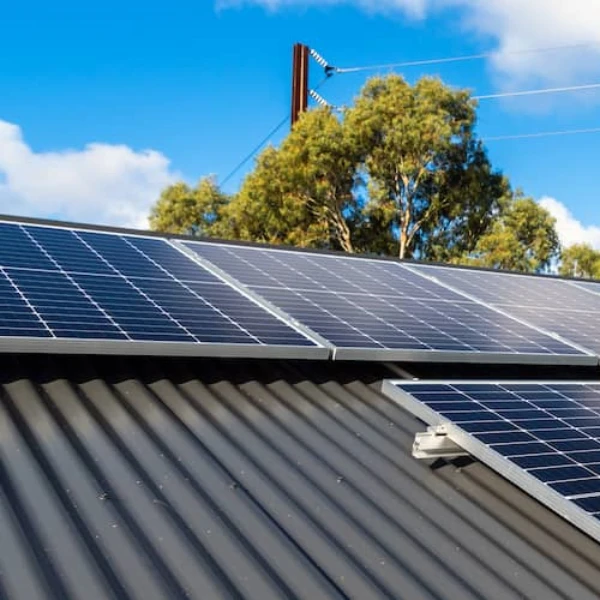

Solar energy is one of the most effective ways to reduce energy costs and environmental impact. When it comes to installing solar panels, homeowners and businesses usually face one key decision: should you go for a ground-mounted or a roof-mounted solar system? Both options have pros and cons, and the right choice depends on your property, budget, and energy goals.
What Is a Roof-Mounted Solar System?
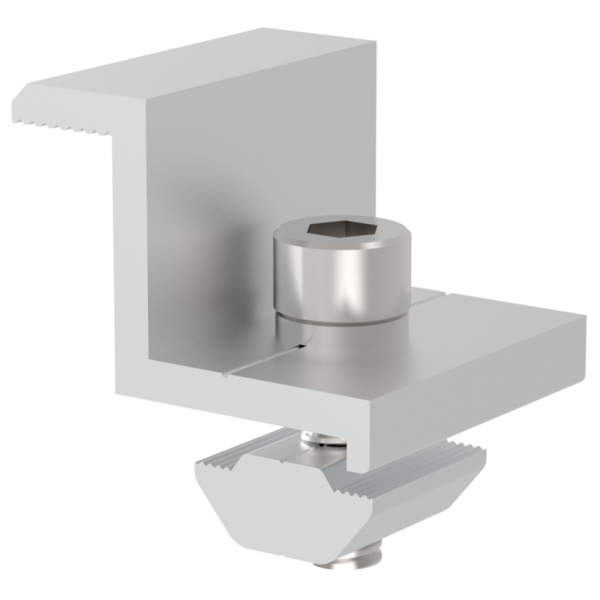
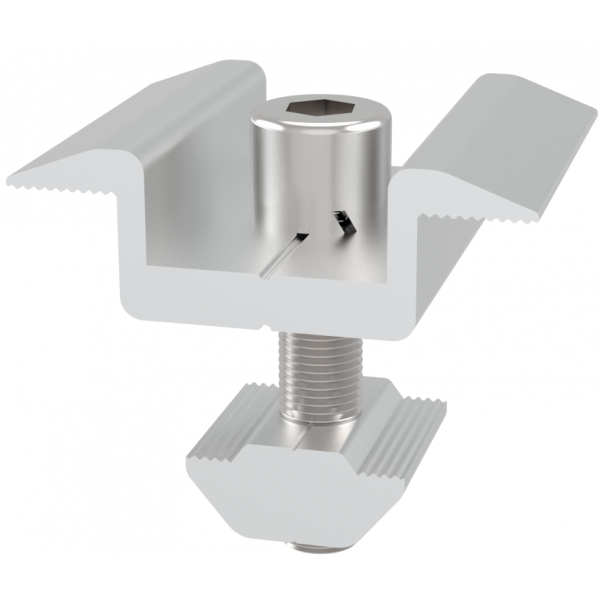
Roof-mounted solar panels are installed directly on the roof of a home or building. This is the most common type of solar installation for residential properties. Roof mounts can be fixed or tilted, depending on the roof’s angle and direction.
Pros of Roof-Mounted Solar:
Space-Saving: Uses existing roof space, freeing up your yard.
Lower Installation Costs: Generally cheaper than ground-mounted systems due to no need for additional foundations.
Quick Installation: Fewer construction requirements make the process faster.
Cons of Roof-Mounted Solar:
Limited Flexibility: Roof orientation and tilt may not be ideal for maximum sunlight.
Roof Condition: Older roofs may need repairs or replacement before installation.
Maintenance Access: Cleaning and maintenance can be harder, especially on steep roofs.
What Is a Ground-Mounted Solar System?
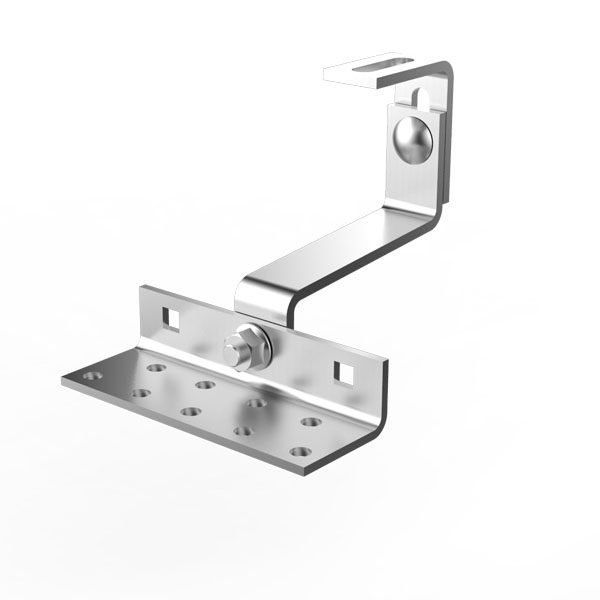
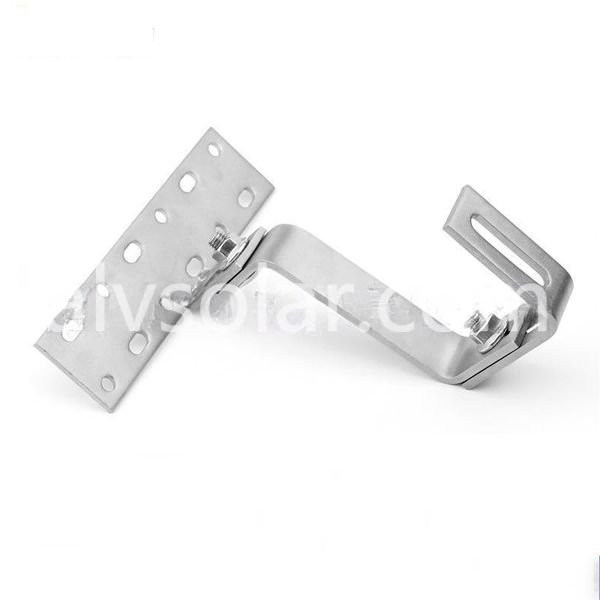
Ground-mounted solar systems are installed on the ground, typically using concrete footings, steel posts, or screw anchors. They can be set at any angle and orientation for optimal sunlight exposure.
Pros of Ground-Mounted Solar:
Optimal Sun Exposure: Can be oriented and tilted to maximize energy production year-round.
Easier Maintenance: Panels are accessible for cleaning and repairs.
Expandable: Easier to add more panels in the future.
Tracking Options: Can include single-axis or dual-axis trackers to increase energy output.
Cons of Ground-Mounted Solar:
Higher Cost: Requires additional materials for foundations and mounting structures.
Space Requirement: Needs a large open area free from shading.
Permits and Zoning: Some areas may have stricter regulations for ground installations.