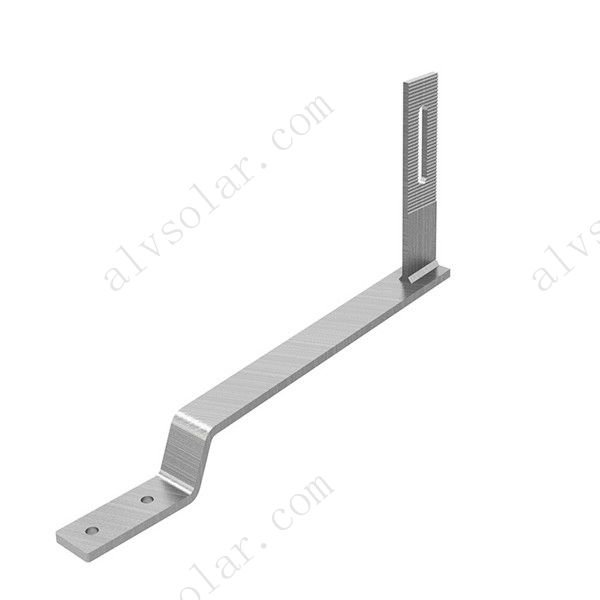
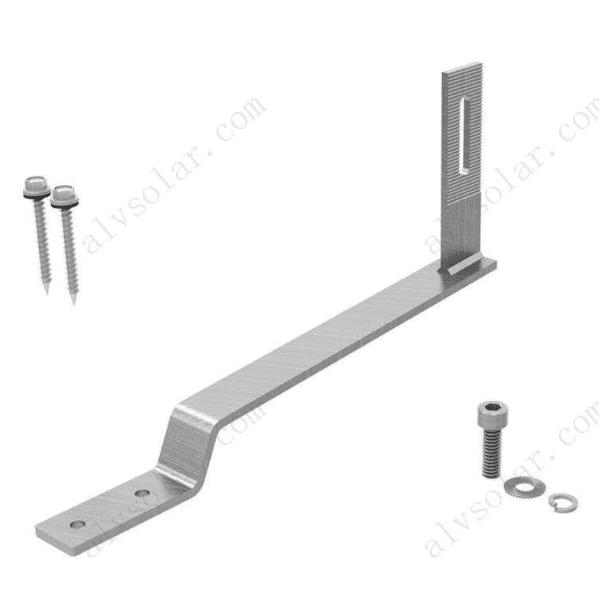
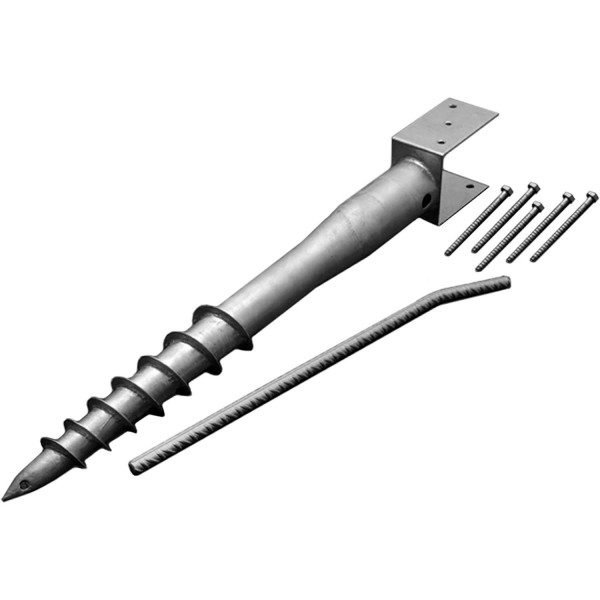
W-Type Solar Ground Mounting System – Durable, Stable, and Terrain-Friendly
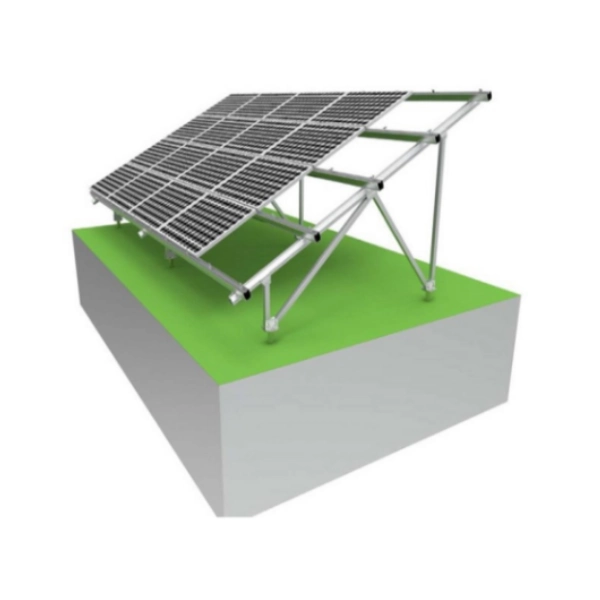
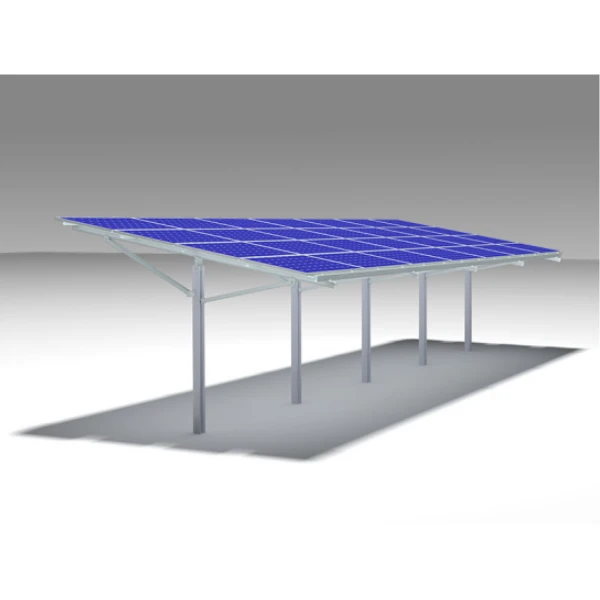
The W-type solar ground mounting system features a dual-pole triangular design with diagonal bracing, forming a unique “W” shape for enhanced structural integrity and wind resistance.
Designed for ground installations on uneven or mountainous terrain, this system is also ideal for large-scale solar power plants where stability and resistance to deformation are critical.
Get a Quote
Key Features
Enhanced Structural Stability
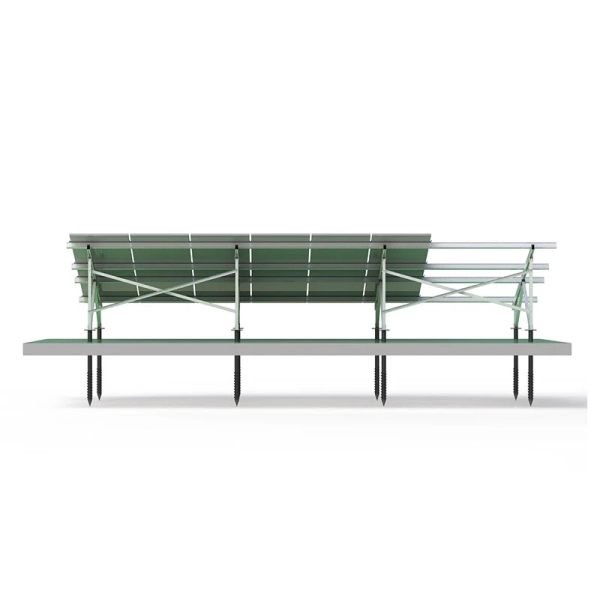
The reinforced “W” frame ensures a strong connection between front and rear poles, minimizing structural distortion and improving load resistance. It can withstand extreme weather conditions, making it suitable for utility-scale solar farms.
Quick Installation with Superior Pre-Assembly
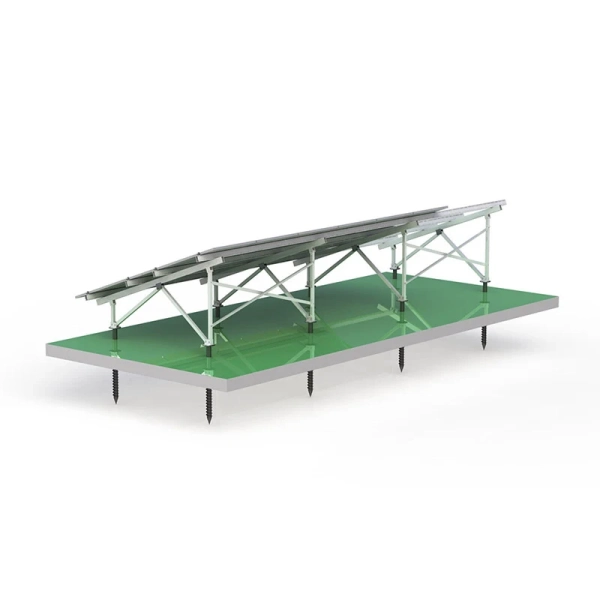
All components come pre-cut and pre-drilled for fast assembly on site. No welding or cutting is required during installation—just lock and secure.
Adaptable to Complex Terrain
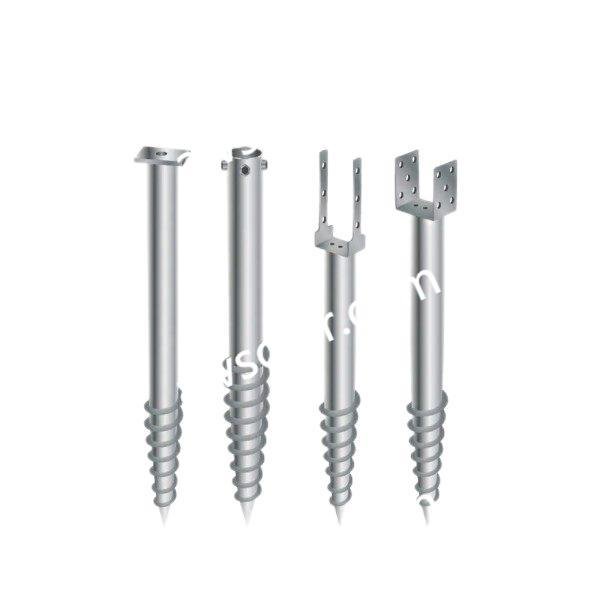
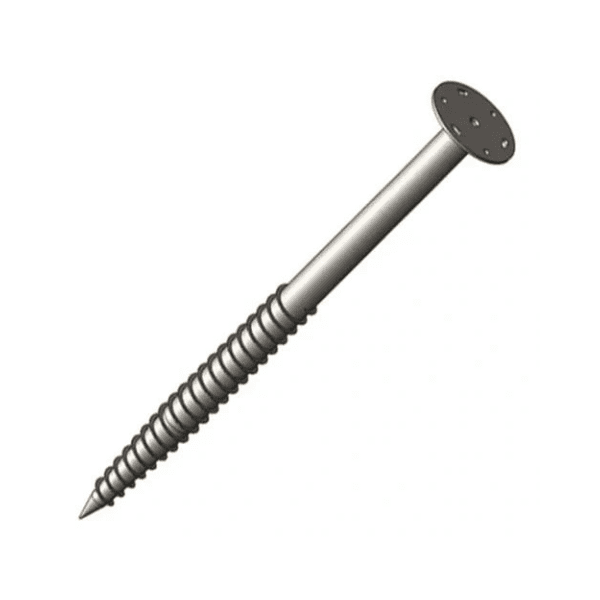
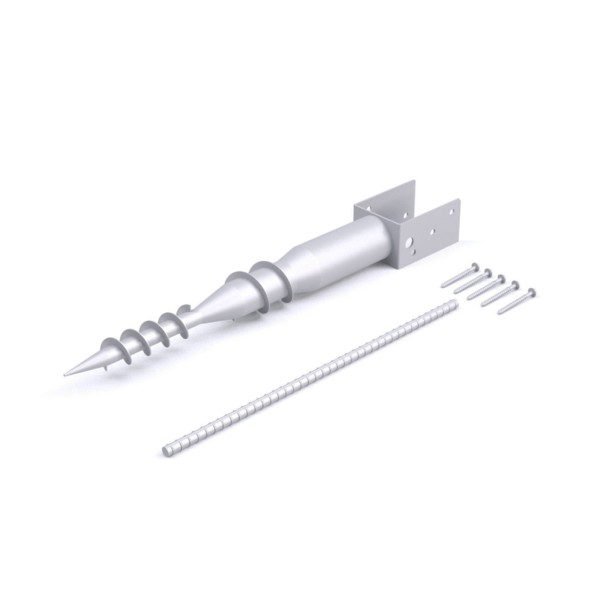
The adjustable tilt angle and flexible foundation options (concrete or ground screw) make it compatible with flatlands, slopes, and rugged surfaces.
Durable and Corrosion-Resistant
Made from anodized aluminum and stainless steel, the system is built to last with superior weather and rust resistance, ensuring long-term performance.
Technical Specifications
| Installation Site |
Ground or Roof |
| Foundation Type |
Concrete or Ground Screw |
| Malzeme |
Aluminum 6005-T5 & Steel |
| Surface Finish |
Anodized Aluminum & Stainless Steel |
| Tilt Angle |
0°–60° |
| Rüzgar Yükü |
≤ 60 m/s |
| Kar Yükü |
≤ 1.8 kN/m² |
| Color |
Natural or Customized |
| Standards |
AS/NZS 1170.2, JIS C 8955:2011 |
| Garanti |
10 Years Warranty, 25 Years Service Life |
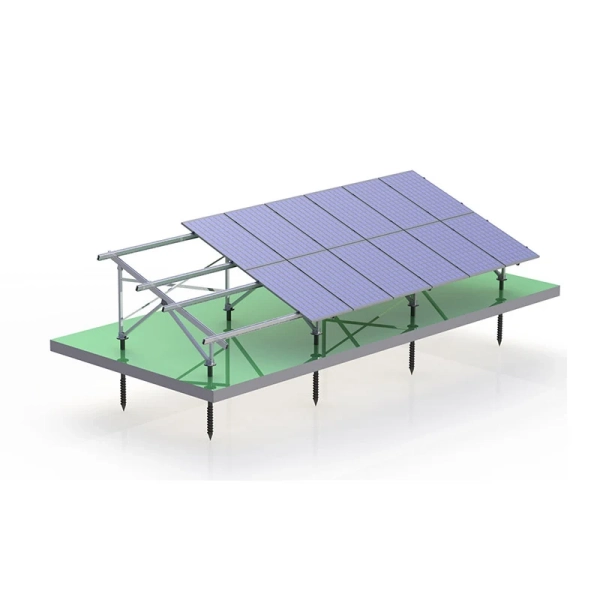
System Components
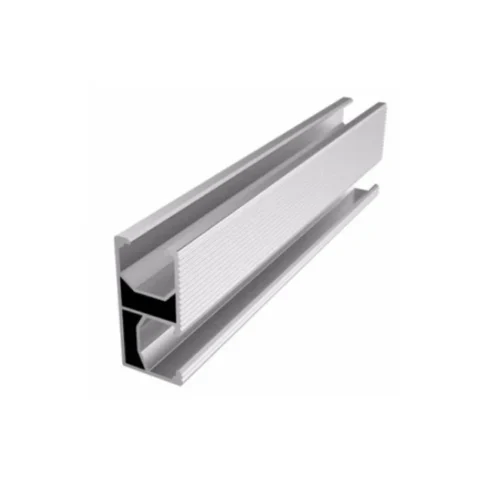
- Rail – Aluminum rail for module support
- Rail Splice – Connects two rail sections seamlessly
- Mid Clamp – Secures solar modules between each other
- End Clamp – Fixes the outermost panels on the array
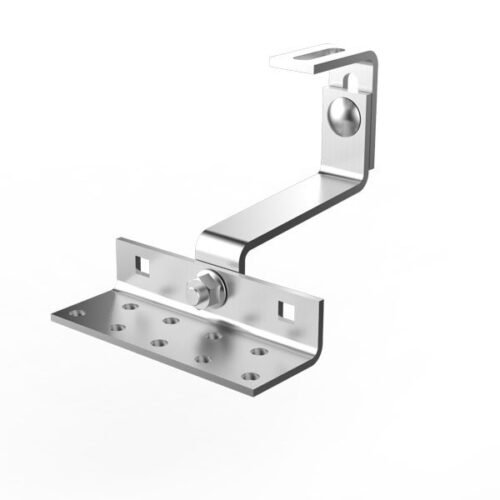
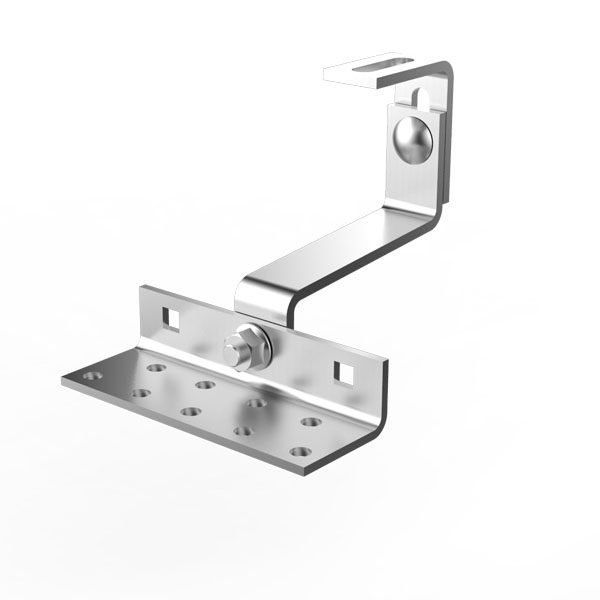
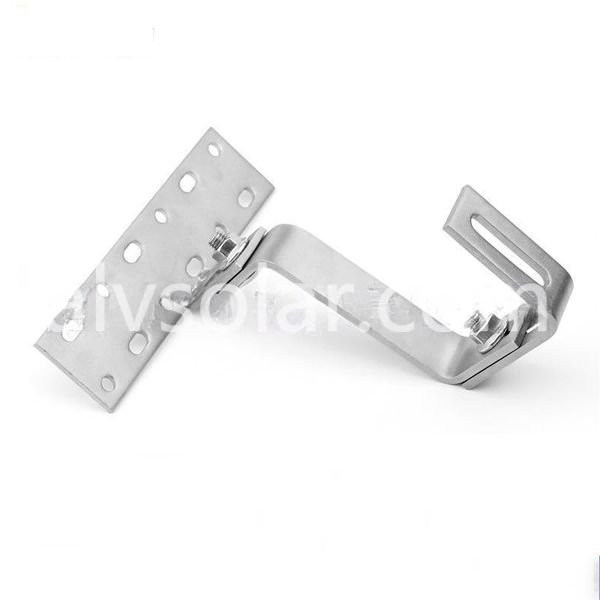
- Foot Base – Anchoring base for the pole structure
- Rail Clamp – Fastening point between rail and structure
- Beam – Transverse structural element for load distribution
- Pole – Main vertical support of the “W” structure
W-Type Solar Mount – FAQ
What makes W-type mounts better than triangular brackets?
The W structure uses more material for greater support and durability, especially in high-wind and high-snow-load environments. It’s preferred for utility-scale projects requiring long-term strength.
What should be considered for residential solar ground mounting?
- Soil Conditions – Conduct a soil test to choose between ground screw or concrete foundation.
- System Size – Determine energy demand and required panel quantity.
- Tilt Angle – Adjust angle based on latitude for optimal solar gain.
- Shading – Avoid trees or structures that may block sunlight.
What are common materials used in solar ground mounting?
- Aluminum Alloy – Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, ideal for most conditions.
- Steel (Hot-dip Galvanized) – Strong and stable, suited for harsh climates.
- Flexible Steel Frames – For irregular terrains like forests, mountains, or ponds.
Where can ground-mounted solar systems be used?
- Open Fields – Ideal for farms and large lands.
- Industrial Facilities – Warehouses, factories, schools, etc.
- Residential Land – For homeowners with large yards or gardens.
- Solar Farms – For grid-scale solar power generation.
What types of ground mounting systems are available?
- Single-Pole – Compact “L” shape, good for small setups.
- Double-Pole – Stronger “T” design for larger installations.
- Frame-Based – Fully customizable, multi-support design.
What are the two main types of ground-mounted installations?
- Standard Ground Mount – Fixed tilt structures anchored to the ground (e.g., concrete base or screw piles).
- Pole-Mount Solar – Elevated poles, often with trackers for maximizing sun exposure.
What are the structural differences between ground and rooftop solar systems?
Ground-Mounted: Uses freestanding frames anchored into soil or concrete. Higher flexibility, requires more space and parts.
Rooftop: Uses roof-mounted hooks or ballasts. More compact and cost-effective but limited by roof shape and load capacity.
Contact Us